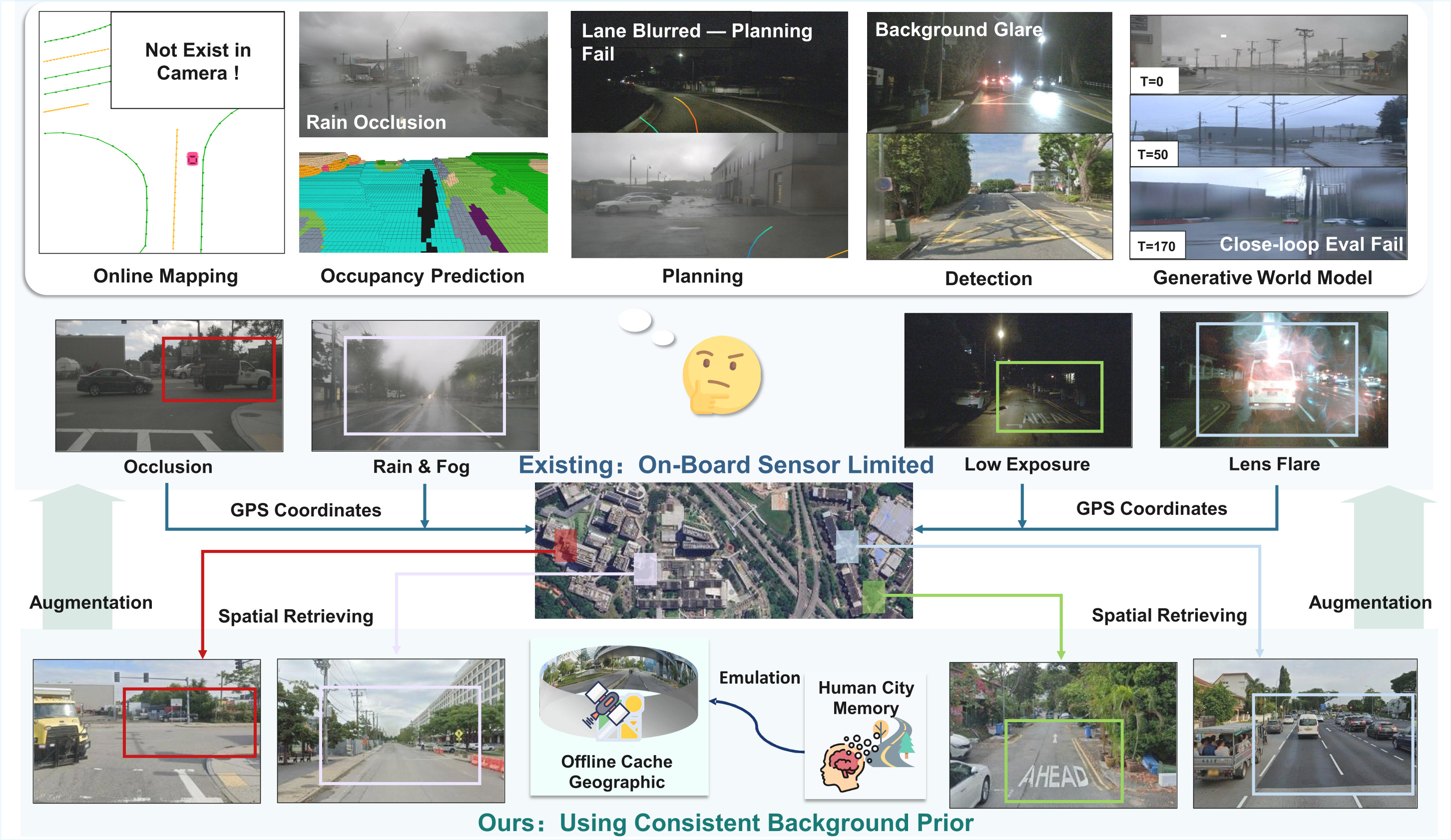
Abstract
For experiments, we first extend the nuScenes dataset with geographic images retrieved via Google Maps APIs and align the new data with ego-vehicle trajectories. We establish baselines across five core autonomous driving tasks: object detection, online mapping, occupancy prediction, end-to-end planning, and generative world modeling. Extensive experiments show that the extended modality could enhance the performance of certain tasks. We will open-source dataset curation code, data, and benchmarks for further study of this new autonomous driving paradigm.
nuScenes-Geography Dataset
The dataset and development toolkit are publicly available:
- Dataset: nuScenes-Geography-Data on Hugging Face
- Devkit: SpatialRetrievalAD-Dataset-Devkit on GitHub
Task Baselines
| Task | Repository |
|---|---|
| Generative World Modeling | Generative-World-Model |
| End-to-End Planning | End2End-Planning |
| Online Mapping | Online-Mapping |
| Occupancy Prediction | Occupancy-Prediction |
| Object Detection | 3D-Detection |
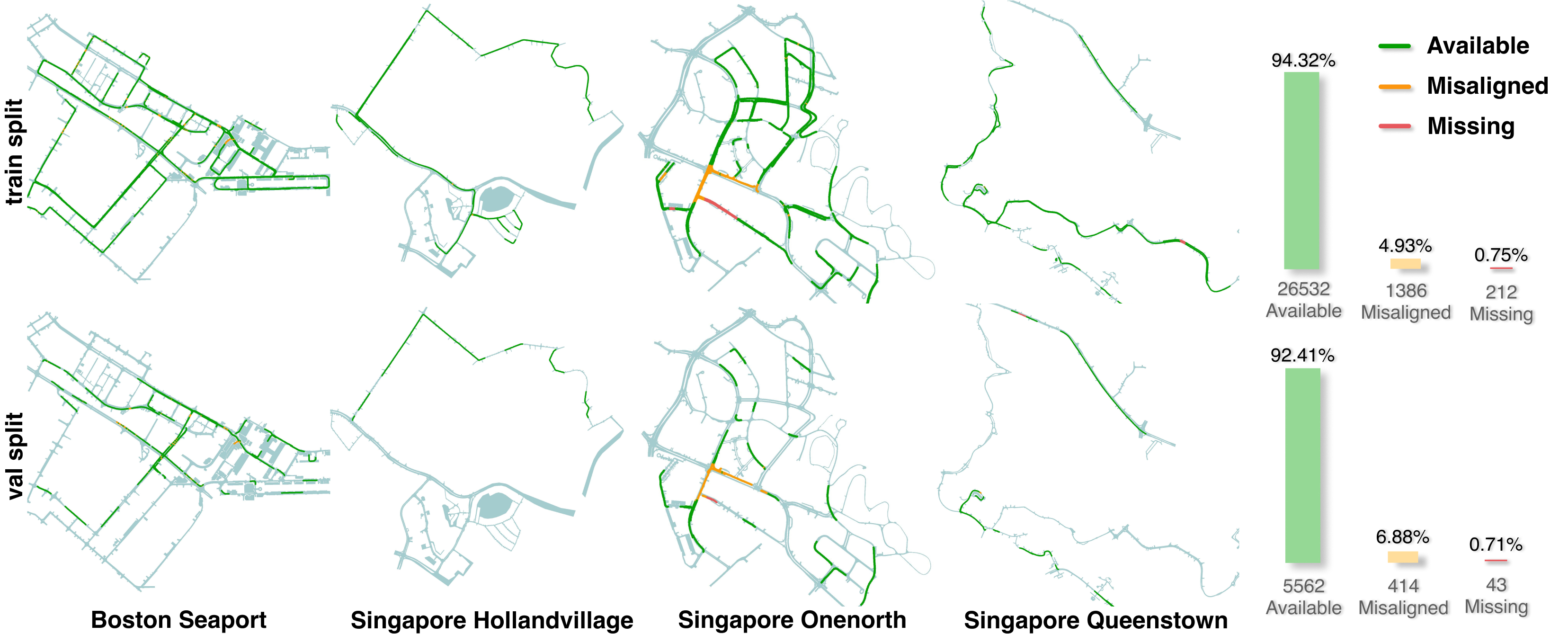
Dataset Visualization
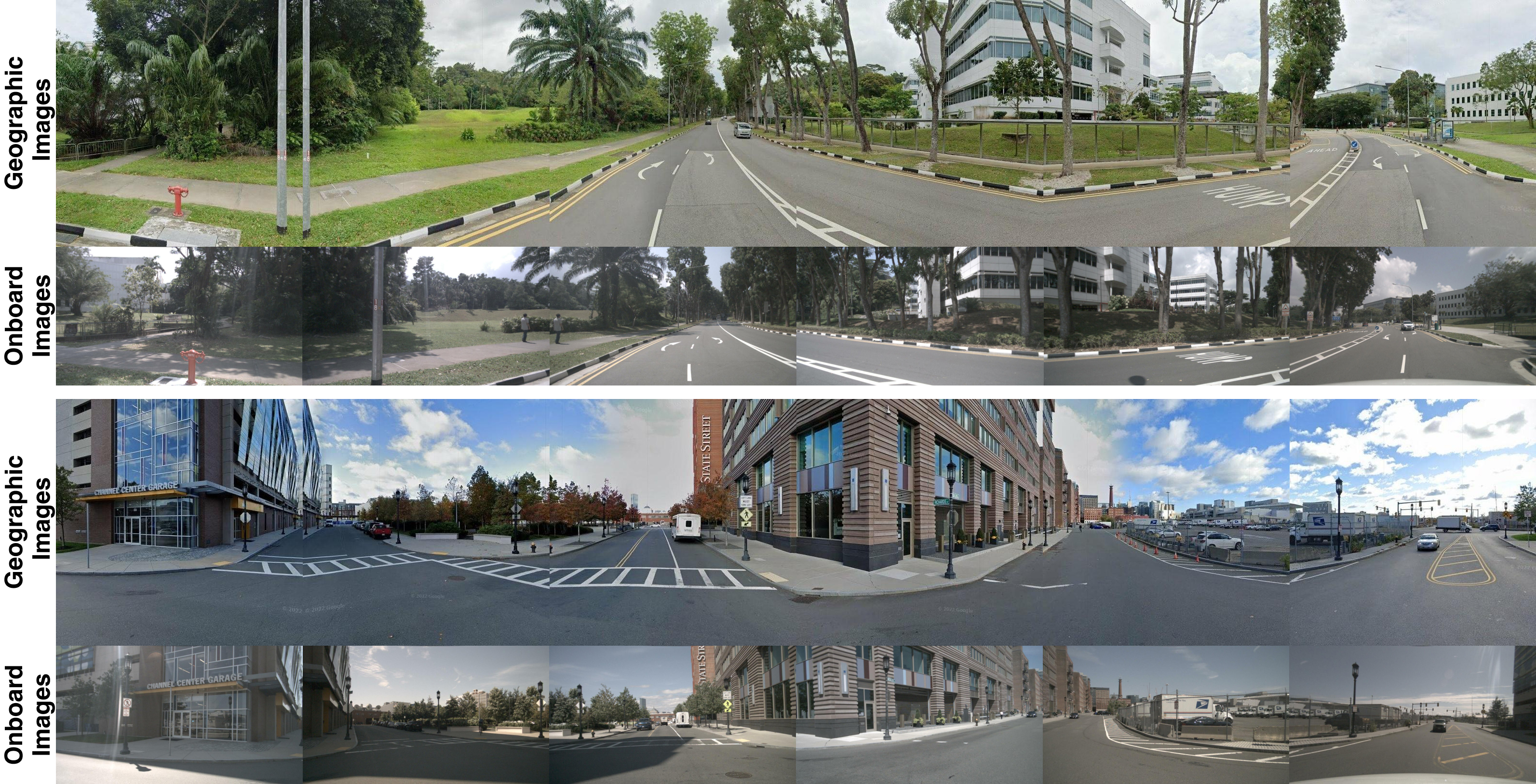
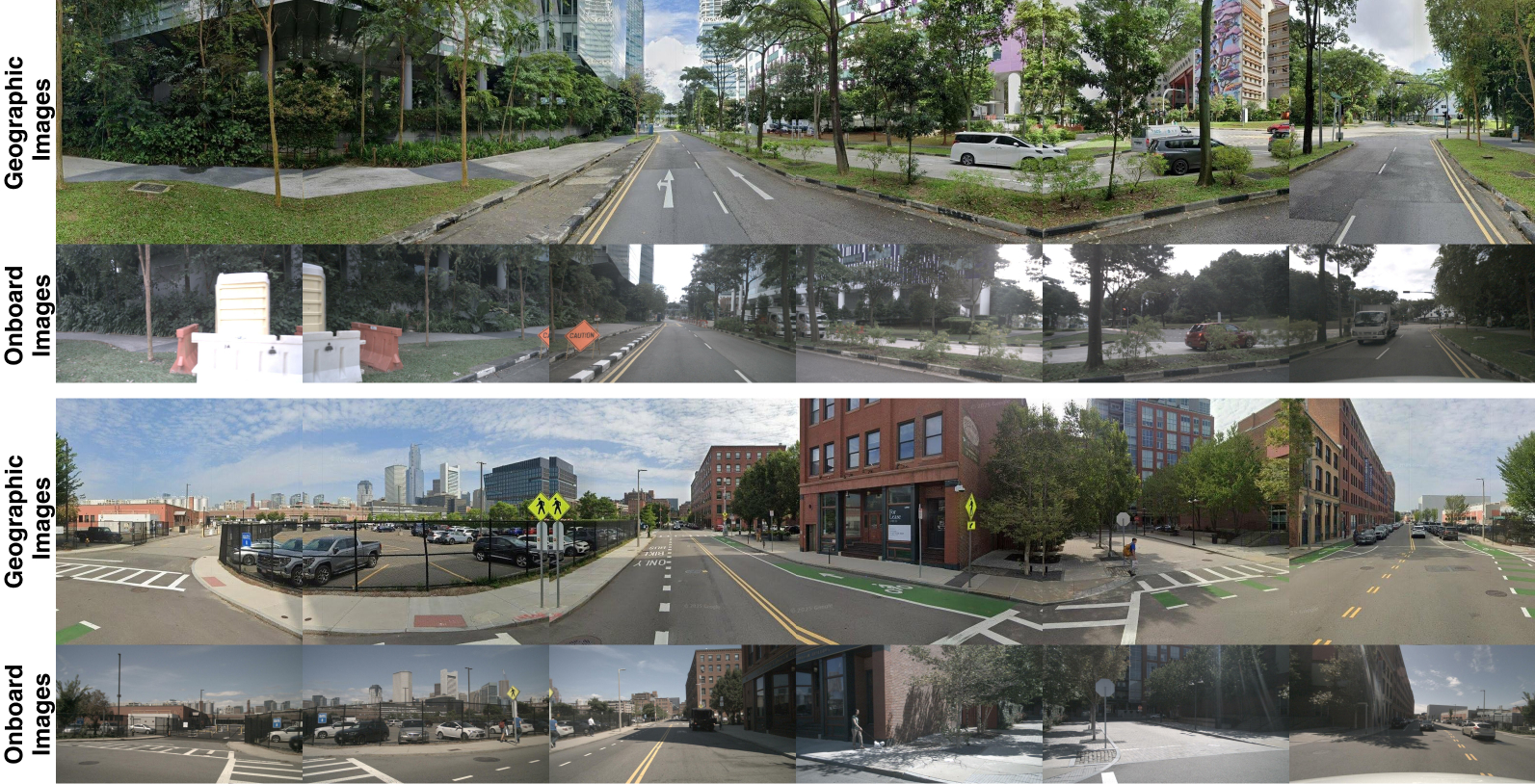
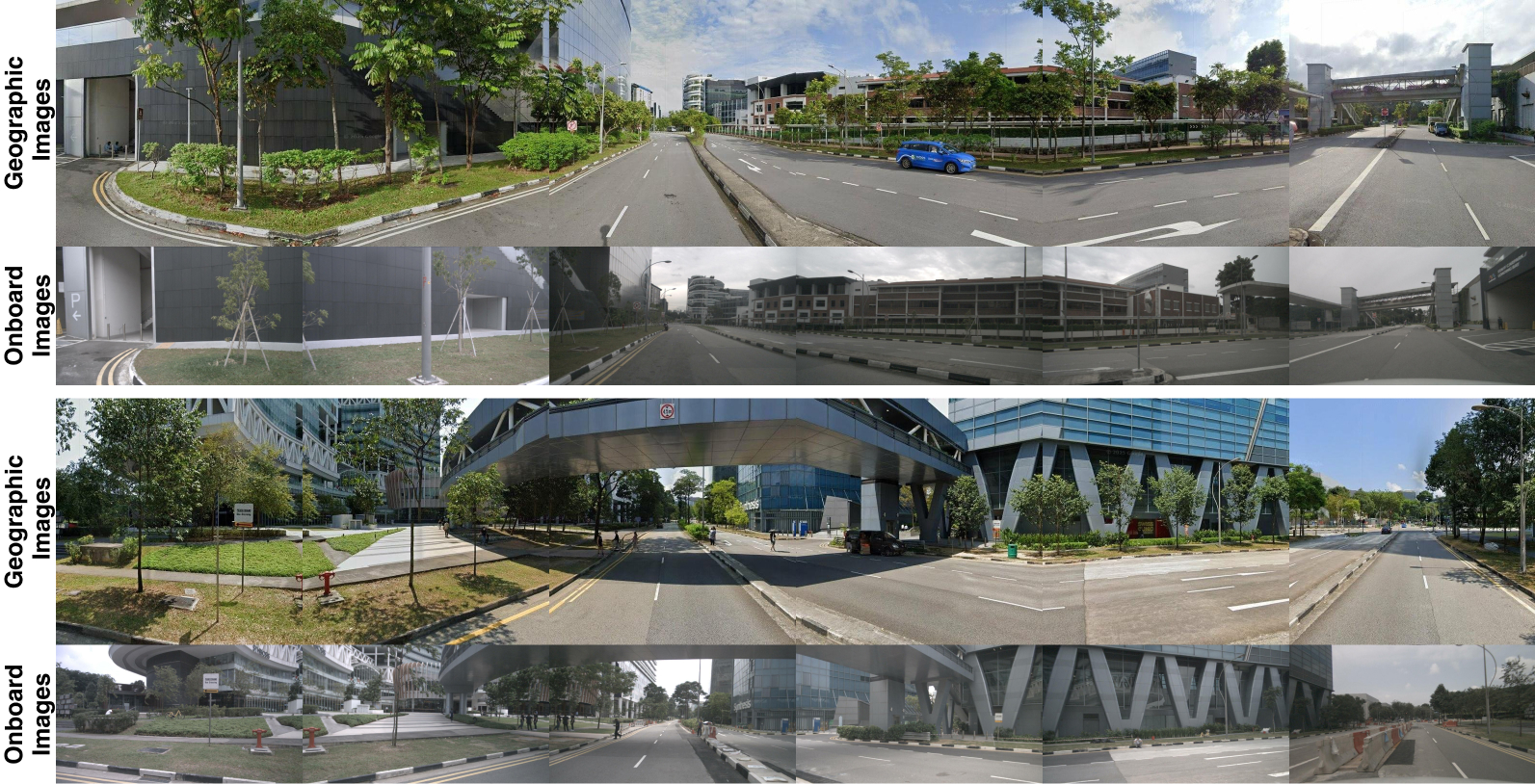



Comparison
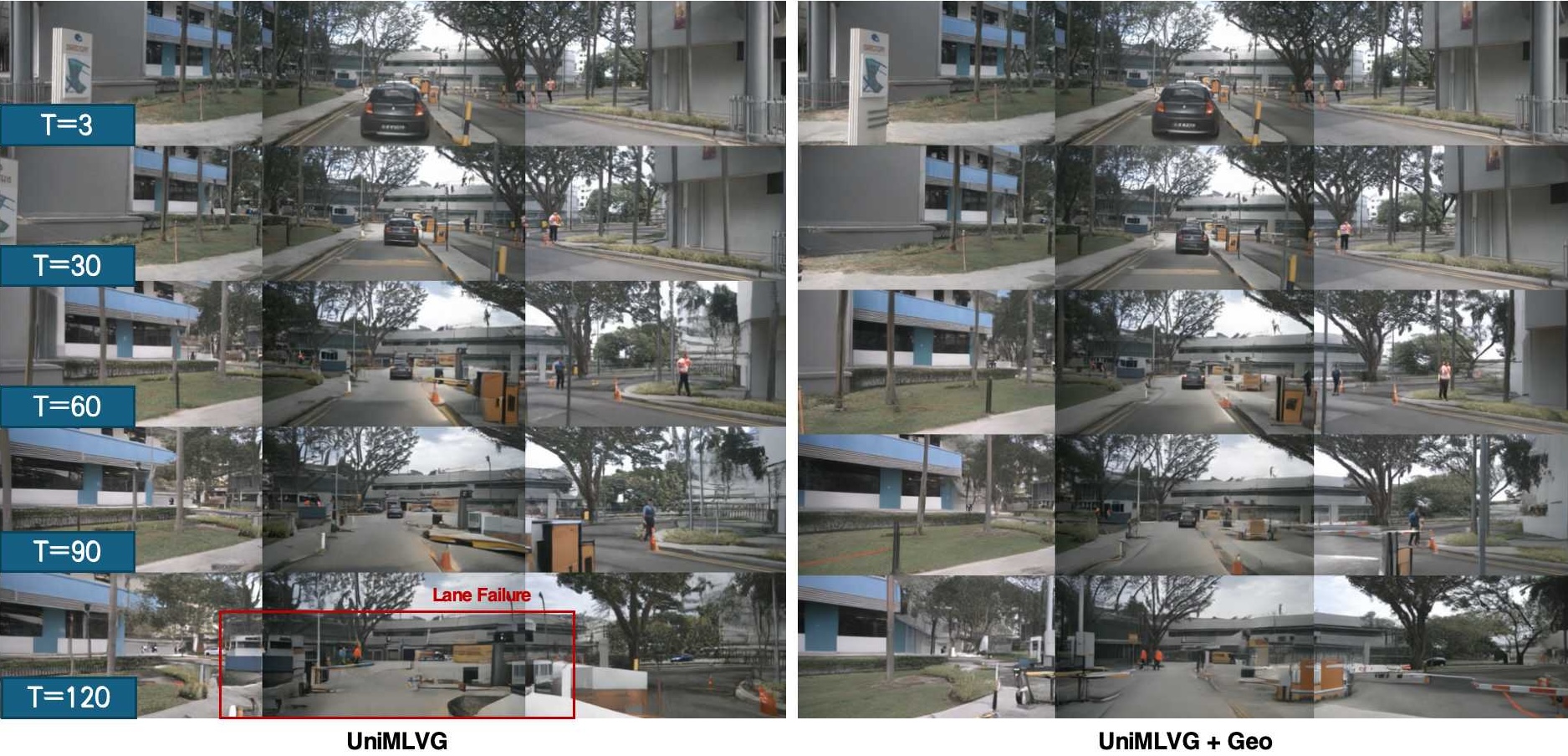
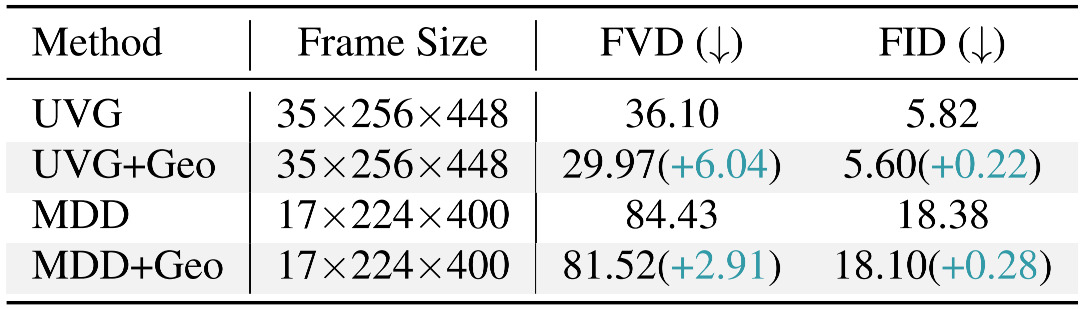
Generative World Model Results. Conditioning UniMLVG and MagicDriveDiT on geographic images leads to lower FVD and FID, effectively preventing scene drift and preserving geometric consistency during rollouts. This demonstrates that spatial retrieval provides a structural scaffold for coherent world modeling.

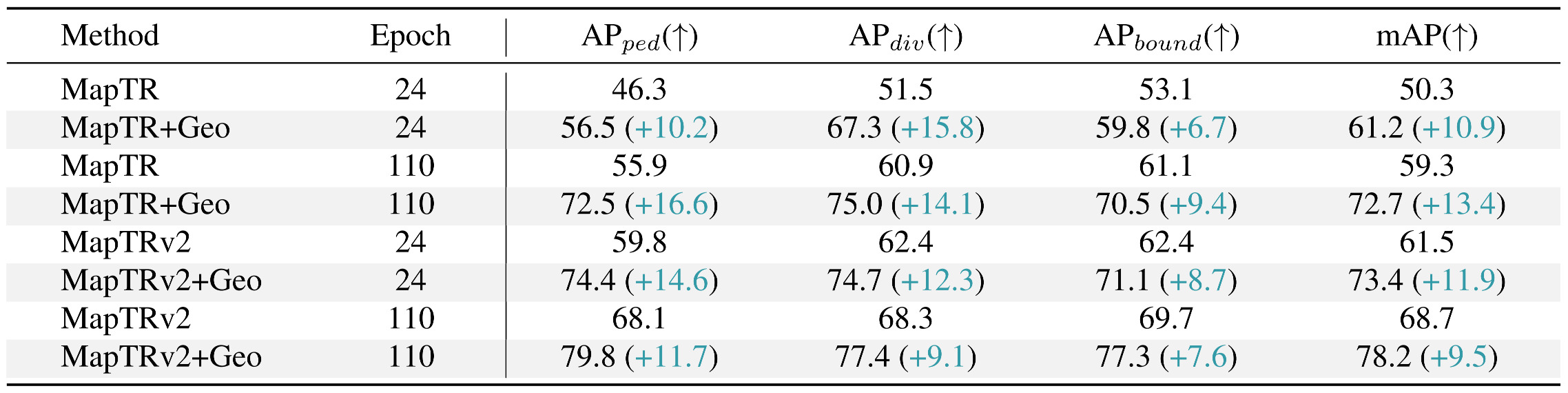
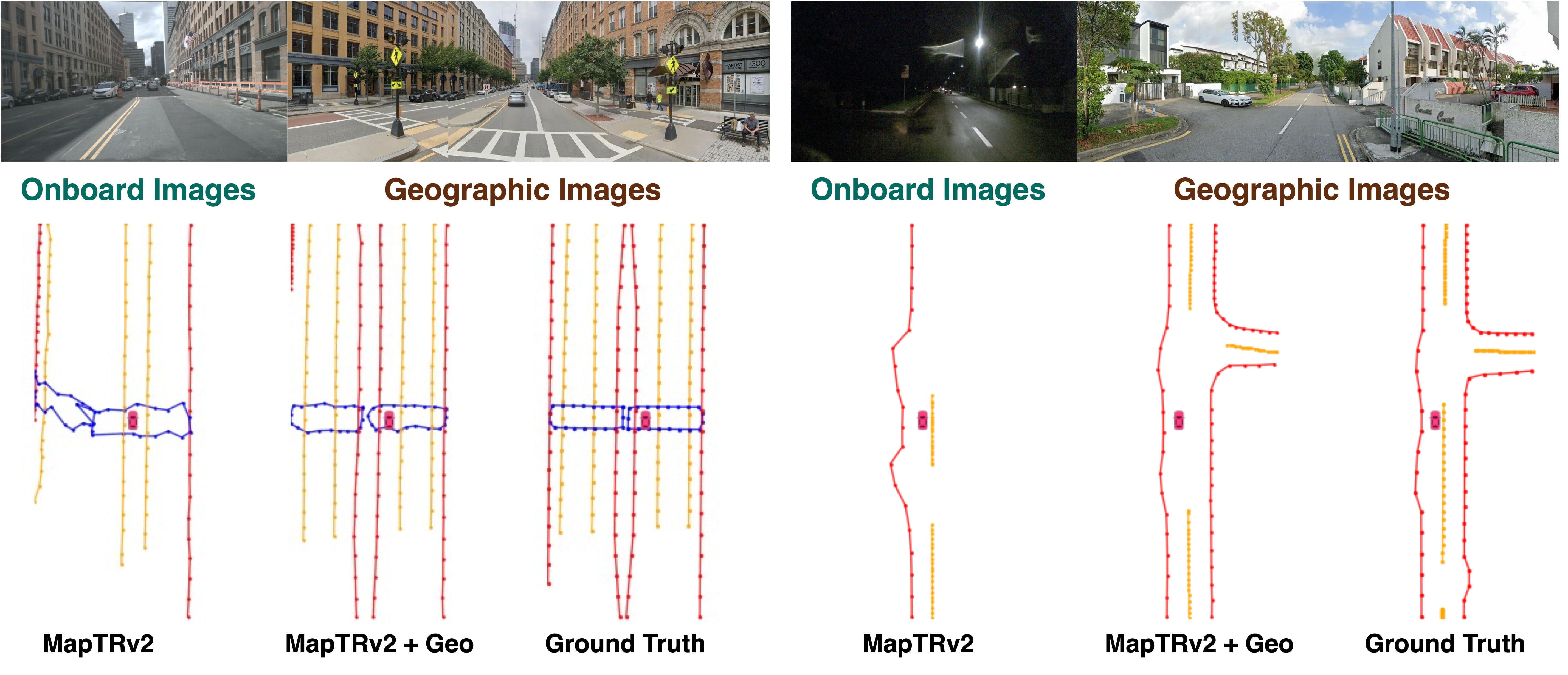
Online Mapping Results. Integrating geographic priors into MapTR and MapTRv2 substantially improves online mapping. The extra background information enables recovery of occluded lanes.
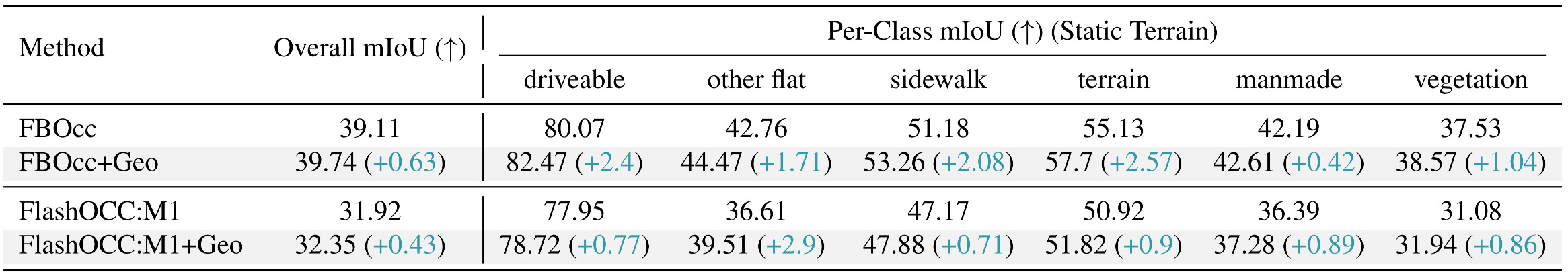
Occupancy Results. Extending FB-OCC and FlashOCC yields consistent mIoU improvements, particularly on static categories. The incorporation of geographic priors further boosts mIoU on static terrain, as they provide additional background information.

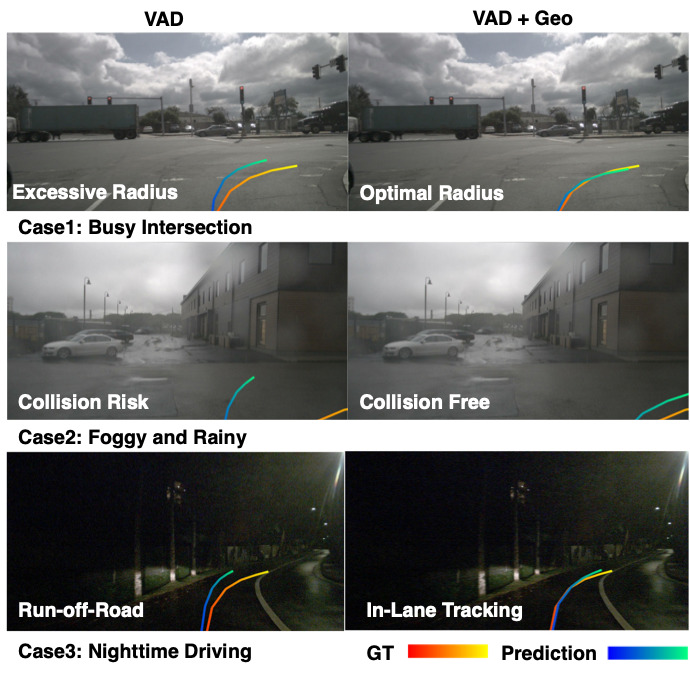
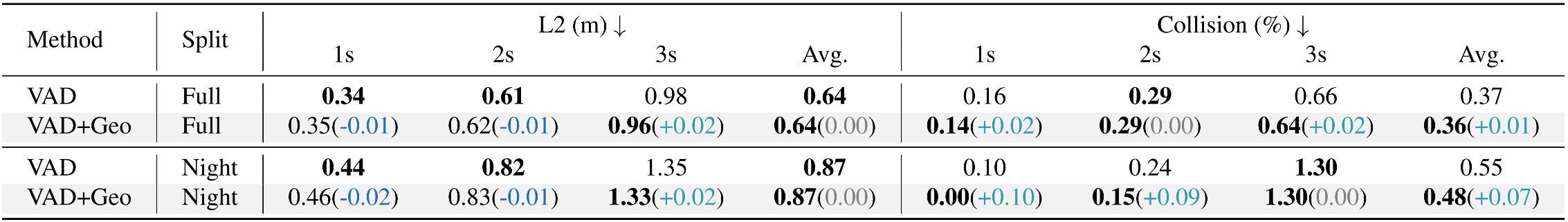
End-to-end Planning Results. We evaluate how spatial retrieval improves safe planning with VAD. Geographic priors provide stable road-layout information, compensating for sensing failures under occlusion or low light. With similar trajectory accuracy, our method achieves better safety margins, reducing the collision rate from 0.55% to 0.48% in challenging night scenes.

Conclusion
Citation
If you use SpatialRetrievalAD in your research, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{jia2026spatial,
title={Spatial Retrieval Augmented Autonomous Driving},
author={Xiaosong Jia and Chenhe Zhang and Yule Jiang and Songbur Wong and Zhiyuan Zhang and Chen Chen and Shaofeng Zhang and Xuanhe Zhou and Xue Yang and Junchi Yan and Yu-Gang Jiang},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year={2026}
},
}